Viktig artikkel fra Leon Chaitow om pustens rolle i ryggsmerter. Beskriver hva som skjer med nervesystemet, med bindevevet og muskelkontroll i ryggraden. Og nevner hvordan progesteron og blodsukker påvirker pusten.
http://leonchaitow.com/wp-content/uploads/pdfs/Breathing%20Pattern%20Disorders%20and%20back%20pain.pdf
«Nixon and Andrews16 have summarised the emerging symptoms resulting from hypocapnoea in a deconditioned individual, as follows: “Muscular aching at low levels of effort; restlessness and heightened sympathetic activity; increased neuronal sensitivity; and, constriction of smooth- muscle tubes (e.g. the vascular, respiratory and gastric- intestinal) can accompany the basic symptom of inability to make and sustain normal levels of effort.” »
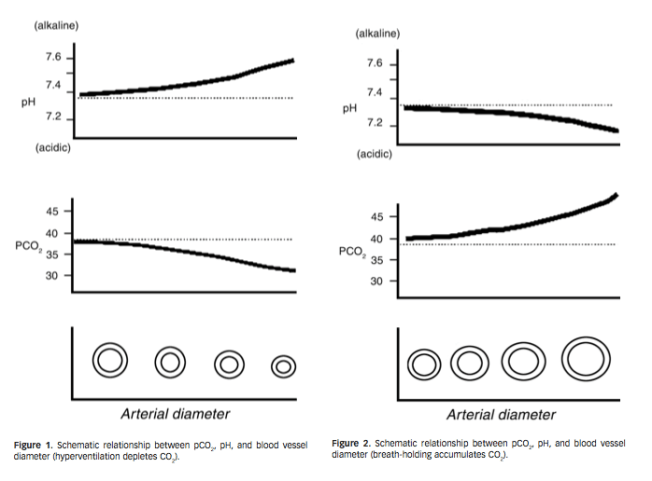
«Lum7 notes, “Alkalosis alone cannot fully explain the symptoms [of chronic hyperventilation]. Altitude adaptation allows residents of high altitudes to remain well, despite chronic respiratory alkalosis. In symptomatic hyperventilation however, the PCO2 fluctuates, often wildly, causing constantly changing pH in nerve cells and tissue fluid to which no adaptation is possible…significant amounts of CO2 can be lost in a few minutes of overbreathing, immediately causing respiratory alkalosis. Compensation, by excretion of bicarbonate, is relatively slow and may take hours or days.” »
«Seyal et al36 note that hyperventilation increases the excitability of both cutaneous and motor axons, and that in experimental animals, HVS increases excitability of hippocampal neurons. Their research, involving healthy humans, demonstrates that hyperventilation increases the excitability of the human corticospinal system. »
«Lum 38 reports,: “During moderate hyperventilation, loss of CO2 ions from neurons stimulates neuronal activity, causing increased sensory and motor discharges, muscular tension and spasm, speeding of spinal reflexes, heightened perception (photophobia, hyperacusis) and other sensory disturbances. More profound hypocapnoea, however, increasingly depresses activity. This parallels the clinical state: initial alertness with increased activity, progressing through decreased alertness, to stupor and coma.” »
«An altered pH in the local chemical environment of peripheral nociceptors, such as occurs with respiratory alkalosis, helps to induce mechanical sensitisation and ischaemic pain.47,48 »
«Hodges further hypothesises: “Although investigation of spinal mechanics is required to confirm the extent to which spinal control is compromised by increases in respiratory demand, it is hypothesised that such a compromise may lead to increased potential for injury to spinal structures and reduced postural control. During strenuous exercise, when the physical stresses to the spine are greater, the physiological vulnerability of the spine to injury is likely to be increased.”
«Progesterone is a respiratory stimulant, making patients with BPD most vulnerable during the post-ovulation phase of the menstrual cycle.10 »
«Blood sugar levels are, “clinically the most important of these non-ventilatory factors. When blood glucose is below the middle of the normal range (i.e. below 4.4 mmol/L) the effects of overbreathing are progressively enhanced at lower levels.” 81 «