Stikkordarkiv: trening
Investigation of the mechanical properties of the human crural fascia and their possible clinical implications.
Om at bindevevet kan endres med stretching over 120s, og kan dermed redusere sitt «stress» med 40%.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23793789
The stress relaxation tests showed that the crural fascia needs 120 s to decrease stress of 40 %, suggesting a similar time also in the living so that the static stretching could have an effect on the fascia
Apnea: A new training method in sport?
Veldig viktig studie om hva dykkeres trening i Apnea (å holde pusten) kan bidra med i annen idrett. Bekrefter det meste av det jeg har skrevet om, men oppklarer noe om blodverdier bl.a. Nevner EPO, nyrenes tilpasning, hypoxi, HIF-1, melkesyre, lungevolum
http://www.univ-rouen.fr/servlet/com.univ.utils.LectureFichierJoint?CODE=1307716204012&LANGUE=0
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19850416
Breath-hold divers have shown reduced blood acidosis, oxidative stress and basal metabolic rate, and increased hematocrit, erythropoietin concentration, hemoglobin mass and lung volumes. We hypothesise that these adaptations contributed to long apnea durations and improve performance. These results suggest that apnea training may be an effective alternative to hypo- baric or normobaric hypoxia to increase aerobic and/or anaerobic performance.
Apnea durations clearly increase with training. Perhaps less well known are the findings that apnea train- ing also increases hematocrit (Hct), erythropoietin (EPO) concen- tration, hemoglobin (Hb) mass, and lung volumes [2–5]. In addition, blood acidosis and oxidative stress were shown to be re- duced after three months of apnea training [6,7]. Therefore, why not encourage apnea training for athletes?
The major determinant of aerobic performance is the capacity to deliver oxygen to the tissues [8]. An increase in the total amount of erythrocytes, as reflected by increased Hct and Hb mass, is med- iated by the glycoprotein hormone EPO, which is predominantly synthesized by the kidneys in response to chronic hypoxia [9] and to some extent (10–15% of total production) by the liver. EPO stimulates the proliferation and maturation of red blood cell precursors in bone marrow, increasing oxygen delivery to muscle and thereby enhancing sports performance [9].
(hypoxic or ischemic conditions) results in a stabilization of the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1a, which increases EPO secretion and the expression of EPO receptor [10].
Furthermore, any training effect vanishes rapidly (two weeks), as the newly formed red cells disappear within a mat- ter of days due to neocytolysis.
The splenic contraction effect
Apnea training may well be a future training method. Splenic contraction has been described in marine mammals as improving oxygen transport, through an increase in circulating erythrocytes. Its consequence is a prolonged dive without injuries. In humans, repeated apneas (five, in general) induce splenic contraction. This increases Hct and Hb (both between 2% and 5%) independently of hemoconcentration [19] and reduces arterial oxygen desaturation, thereby prolonging the apnea duration [3,19–22].
Repeated apneas are known to induce hypoxemia in the spleen and kidney, increas- ing respectively Hct and Hb and serum EPO concentrations [2,23].
First, the splenic contraction develops quickly after three or four apneas separated by two minutes of recovery and is associ- ated with a transient increase in Hb concentration. The amplitude of the spleen volume reduction after repeated apneas, with or without face immersion, varies widely (20–46%) depending on the rate of change in oxygenation [3,19,22,25–27]. The rapidity of the splenic contraction after simulated apneas strongly suggested a centrally-mediated feed-forward mechanism rather than the influ- ence of slower peripheral triggers [19]. These spleen and Hb re- sponses may be trainable.
Second, DeBruijns et al. [2] recently observed that repeated apneas increased EPO concentration by 24%, with the peak value reached 3 h after the last apnea and a return to baseline 2 h later.
The rapid reduction in tissue oxygen levels that oc- curs during apneas has been suggested to stimulate enhanced EPO production [25]. The decreased kidney blood flow induced by apneic vasoconstriction would result in local ischemic hypoxia, stimulating kidney EPO production. Similarly, obstructive sleep ap- nea increases the levels of EPO (1.6) and Hb (+18%) [24].
The lower SaO2 decrease found in trained divers after repeated apneas may account for the reduced oxygen delivery because of the diving response (bradycardia and vasocon- striction) and/or an increase in oxygen content [1].
Long term-effects
Another important consideration is the persistence of the per- formance gains. Most of the altitude exposure studies reported short-term effects (i.e., weeks). Repeated apneas increase Hct but this increase disappears within 10min after the last apnea [22,26].
The effects of repeated apneas on spleen and endogenous EPO may also constitute an alternative to using rhEPO or its analogues. In addition, comparison of resting Hb mass in elite BHDs and untrained subjects showed a 5% higher Hb mass in the BHDs, and the BHDs also showed a larger relative increase in Hb after three apneas (2.7%). The long-term effect of apnea training on Hb mass might be implicated in elite divers’ performances. Re- cently, it has been found that after a 3-month apnea training pro- gram, the forced expiratory volume in 1 s was higher (4.85 ± 0.78 vs. 4.94 ± 0.81 L, p < 0.05), with concomitant increases in the max- imal oxygen uptake, arterial oxygen saturation, and respiratory compensation point values during an incremental test [30].
In addition to increasing EPO and provoking splenic contraction, apnea training has been hypothesized to modify muscle glycolytic metabolism. An improvement in muscle buffer capacity [6,7,32] would reduce blood acidosis and post-apnea oxidative stress [6]. Delayed acidosis would also be advantageous for exercise perfor- mance. Finally, trained BHDs exhibit high lung volumes [15]. Ap- nea training might be interesting to improve respiratory muscle performance [15], thereby delaying the respiratory muscle fatigue during prolonged and maximal exercise.
Greater cerebral blood flow (CBF) increase was described during long apnea in elite BHDs than in controls and interpreted as a protection of the brain against the alteration of blood gas [33]. The CBF increase observed in BHDs could be the re- sult of an increased capillary density in the brain as has been de- scribed after a prolonged hypobaric hypoxia exposure [35]. These results suggest that apnea training per se provides hypoxic precon- ditioning, increasing hypoxemia and ischemia tolerance [33].
The physiological responses to apnea training exhibited by elite breath-hold divers may contribute to improving sports perfor- mance. These adaptations may be an effective alternative to hypo- baric or normobaric hypoxia to increase performance. Further experimental research of the apnea training effects on aerobic and/or anaerobic performance are needed to confirm this theory.
Diaphragmatic Breathing Reduces Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress
Om hvordan diafragmisk pust (med magen) øker antioksidantbeskyttelsen og restitusjonen ved å senke kortison og øke melatonin. Gjort på et 24t sykkerlritt hvor de som gjorde 1t pusteing før de sovnet fikk raskere restitusjon. Nevner direkte sammenheng mellom kortisol og melatonin. Og påstår at pusten bør implementeres i ethvert treningsregime som restitusjon.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3139518/
Analysis of oxidative stress levels in people who meditate indicated that meditation correlates with lower oxidative stress levels, lower cortisol levels and higher melatonin levels. It is known that cortisol inhibits enzymes responsible for the antioxidant activity of cells and that melatonin is a strong antioxidant
Results demonstrate that relaxation induced by diaphragmatic breathing increases the antioxidant defense status in athletes after exhaustive exercise. These effects correlate with the concomitant decrease in cortisol and the increase in melatonin. The consequence is a lower level of oxidative stress, which suggests that an appropriate diaphragmatic breathing could protect athletes from long-term adverse effects of free radicals.
Stress is defined as a physiological reaction to undesired emotional or physical situations. Initially, stress induces an acute response (fight or flight) that is mediated by catecholamines. When stress becomes chronic and lasts for a long time, the stressed organism reacts with physiological alterations to adapt to the unfavorable conditions. This ACTH-mediated reaction affects the immune and neuroendocrine systems, and it is responsible for several diseases [1]. Numerous data support the hypothesis that the pathophysiology of chronic stress can be due, at least partially, to an increase in oxidative stress [2–4], which may also contributes to heart disease [5,6], rheumatoid arthritis [7,8], hypertension [9,10], Alzheimer’s disease [11,12], Parkinson’s disease [13], atherosclerosis [14] and, finally, aging [15].
High levels of glucocorticoids are known to decrease blood reduced glutathione (GSH) and erythrocyte superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in rats [20]. Other enzymes are also involved, and NADPH oxidase, xanthine oxidase and uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase are important sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in glucocorticoid-induced oxidative stress (see [9] for a review on this argument).
Hormonal reactions to stressors, in particular plasma cortisol levels, are lower in people who meditate than in people who do not [31–36], suggesting that it is possible to modulate the neuroendocrine system through neurological pathways. Analysis of oxidative stress levels in people who meditate indicated that transcendental meditation, Zen meditation and Yoga correlate with lower oxidative stress levels [37–43].
Melatonin could also be involved in the reduction of oxidative stress because increased levels of this hormone have been reported after meditation [44–46]. This neurohormone is considered a strong antioxidant and is used as a treatment for aging. Melatonin in fact, increases several intracellular enzymatic antioxidant enzymes, such as SOD and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) [47,48], and induces the activity of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase, thereby stimulating the production of the intracellular antioxidant GSH (49]. A number of studies have shown that melatonin is significantly better than the classic antioxidants in resisting free-radical-based molecular destruction. In these in vivostudies, melatonin was more effective than vitamin E, β-carotene [50–52] and vitamin C [53–55].
Although it has been established that a continuous and moderate physical activity reduces stress, intense and prolonged exercise is deleterious and needs a proper recovery procedure.
Plasma cortisol levels increase in response to intense and prolonged exercise [60,61]. Ponjee et al. [62] demonstrated that cortisol increased significantly in male athletes after they ran a marathon. In another study, plasma ACTH and cortisol were found elevated in highly trained runners and in sedentary subjects after intense treadmill exercise [63].
Most, if not all, meditation procedures involve diaphragmatic breathing (DB), which is the act of breathing deeply into the lungs by flexing the diaphragm rather than the rib cage. DB is relaxing and therapeutic, reduces stress and is a fundamental procedure of Pranayama Yoga, Zen, transcendental meditation and other meditation practices.
Athletes were monitored during a training session for a 24-h long contest. This type of race lasts for 24 h, generally starting at 10:00
h, generally starting at 10:00 am and ending at 10:00
am and ending at 10:00 am the following day. Bikers ride as many kilometers as possible on a specific circuit trail in the 24-h period. Athletes are allowed to stop, to sleep, to rest and to eat as much food as they want to eat.
am the following day. Bikers ride as many kilometers as possible on a specific circuit trail in the 24-h period. Athletes are allowed to stop, to sleep, to rest and to eat as much food as they want to eat.
Subjects of the studied group were previously trained to relax by performing DB and concentrating on their breath. These athletes spent 1 h (6:30–7:30
h (6:30–7:30 pm) relaxing performing DB in a quiet place. The other eight subjects, representing the control group, spent the same time sitting in an equivalent quite place. The only activity allowed was reading magazines. Lighting levels were monitored throughout the experiment and did not exceed 15 lux, a level well below that known to influence melatonin secretion [73,74].
pm) relaxing performing DB in a quiet place. The other eight subjects, representing the control group, spent the same time sitting in an equivalent quite place. The only activity allowed was reading magazines. Lighting levels were monitored throughout the experiment and did not exceed 15 lux, a level well below that known to influence melatonin secretion [73,74].

As expected, the exercise induced a strong oxidative stress in athletes (Figure 1).

BAP (Biological Antioxidant Potential) levels were determined at different times, before and after exercise. Athletes were divided in two equivalent groups of eight subjects. Subjects of the studied group spent 1 h relaxing performing DB and concentrating on their breath in a quiet place. The other eight subjects, representing the control group, spent the same time sitting in an equivalent quite place. Since this test must be performed several hours after food ingestion, BAP levels were determined pre-exercise at 8:00
h relaxing performing DB and concentrating on their breath in a quiet place. The other eight subjects, representing the control group, spent the same time sitting in an equivalent quite place. Since this test must be performed several hours after food ingestion, BAP levels were determined pre-exercise at 8:00 am before breakfast, at 2:00
am before breakfast, at 2:00 am, and at 8:00
am, and at 8:00 am 24
am 24 h post-exercise. Values shown are mean ± SD. *P < .05 DB versus control group. **P < .01 DB versus control group.
h post-exercise. Values shown are mean ± SD. *P < .05 DB versus control group. **P < .01 DB versus control group.


This study demonstrates that DB reduces the oxidative stress induced by exhaustive exercise. To our knowledge, this is the first study which explores the effect of DB on the stress caused by exhaustive physical activity.

The rationale is as follows (Figure 5)
- intense exercise increases cortisol production;
- a high plasmatic level of cortisol decreases body antioxidant defenses;
- a high plasmatic level of cortisol correlates with a high level of oxidative stress;
- DB reduces the production of cortisol;
- DB increases melatonin levels;
- melatonin is a strong antioxidant;
- DB increases the BAP and
- DB reduces oxidative stress.
If these results are confirmed in other intense physical activity programs, relaxation could be considered an effective practice to significantly contrast the free radical-mediated oxidative damage induced by intense exercise. Therefore, similar to the way that antioxidant supplementation has been integrated into athletic training programs, DB or other meditation techniques should be integrated into many sports as a method to improve performance and to accelerate recovery.
Hyperventilation, in fact, induces hyperoxia which is known to be related with oxidative stress [81,82]. The hyperventilation syndrome affects 15% of the population and occurs when breathing rates elevate to 21–23 bpm as a result of constricted non-DB. DB can treat hyperoxia and its consequences acting by two synergic ways: restoring the normal breath rhythm and reducing oxidative stress mainly through the increase in melatonin production which is known for its ability to reduce oxidative stress induced by exposure to hyperbaric hyperoxia [83].
Moreover, Orme-Johnson observed greatly reduced pathology levels in regular meditation practitioners [84,85]. A 5 years statistic of approximately 2000 regular participants demonstrated that Transcendental Meditation reduced benign and malignant tumors, heart disease, infectious diseases, mental disorders and diseases of the nervous system. Mourya et al. evidenced that slow-breathing exercises may influence autonomic functions reducing blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension [86]. Finally, there are also evidences that procedures which involve the control of the breathing can positively affect type 2 Diabetes [87], depression, pain [88], high glucose level and high cholesterol [89].
The role of melatonin must also be emphasized. Beyond its antioxidant properties, melatonin is involved in the regulation of the circadian sleep-wake rhythm and in the modulation of hormones and the immune system. Due to its wide medical implications, the increase in melatonin levels induced by DB suggests that this breath procedure deserves to be included in public health improvement programs.
DB increased the levels of melatonin in athletes, and this correlates with lower oxidative stress (ROMs), with lower cortisol levels and with the higher antioxidant status (BAP) in these athletes.
Tooley et al. [46] speculated that meditation-reduced hepatic blood flow [91] could raise the plasma levels of melatonin. Alternatively, since meditation increases plasma levels of noradrenaline [92] and urine levels of the metabolite 5HIAA [93], a possible direct action on the pineal gland could be hypothesized, as melatonin is synthesized in the pineal by serotonin under a noradrenaline stimulus [94]. More likely, we suspect that the increase in melatonin levels determined in our experiment can be mainly attributed to the reduced cortisol levels. Actually, a relationship between cortisol and melatonin rhythms has been observed [95], indicating that melatonin onset typically occurs during low cortisol secretion.
Overall, these data demonstrate that relaxation induced by DB increases the antioxidant defense status in athletes after exhaustive exercise. These effects correlate with the concomitant decrease in cortisol, which is known to negatively affect antioxidant defenses, and the increase in melatonin, a strong antioxidant. The consequence is a lower level of oxidative stress, which suggests that an appropriate recovery could protect athletes from long-term adverse effects of free radicals.
Intermittent Hypoxia Research in the Former Soviet Union and the Commonwealth of Independent States: History and Review of the Concept and Selected Applications
Svært viktig review om IHT – intermittend hypoxia training – som det har blitt gjort mye forskning på i russland, men først nå begynt å bli interessant i vesten. Nevner hvordan co2 reageer på hypoxi, og nervesystemet og vevet og i mitchondria, inklidert at SOD øker med 70% og at IHT normaliserer NO som lagres i blodkarene. Om at IHT kan brukes i behandling av sykdommer, inkludert strålingskader fra Chernobyl. Metoden er en «rebreathing» frem til O2% er nede på 7% – ca. 5 minutter daglig i 3 dager.
http://altitudenow.com/images/Hypoxia_in_USSR.pdf
To the present day, intermittent hypoxic training (IHT) has been used extensively for altitude preacclimatization; for the treatment of a variety of clinical disorders, including chronic lung diseases, bronchial asthma, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, Parkinson’s disease, emotional disorders, and radiation toxicity, in prophylaxis of certain occupational diseases; and in sports.
The basic mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of IHT are mainly in three areas: regulation of respiration, free-radical production, and mitochondrial respiration. It was found that IHT induces increased ventilatory sensitivity to hypoxia, as well as other hypoxia-related physiological changes, such as increased hematopoiesis, alveolar ventilation and lung diffusion capacity, and alterations in the autonomic nervous system.
Due to IHT, antioxidant defense mechanisms are stimulated, cellular membranes become more stable, Ca2+ elimination from the cytoplasm is increased, and 02 transport in tissues is improved. IHT induces changes within mitochondria, involving NAD-dependent metabolism, that increase the efficiency of oxygen utilization in ATP production. These effects are mediated partly by NO-dependent reactions.
Particularly at issue are the effects in humans of such transient bouts of hypoxia when repeated many times, a practice designated as intermittent hypoxia. Furthermore, when intermittent hypoxia as a specific protocol is employed to accomplish a particular aim, for example, acclimatization to high altitude, we use the term intermittent hypoxic training or IHT.
The interested reader is referred to more extensive recent scientific and historical reviews and investigative reports in Russian and Ukrainian, particularly as related to the potential thera- peutic effects of intermittent hypoxia (Berezovsky et al., 1985; Karash et al., 1988; Meerson et al., 1989; Anokhin et al., 1992; Berezovskii and Levashov, 1992; Donenko, 1992; Ehrenburg, 1992; Fesenko and Lisyana, 1992; Vinnitskaya et al., 1992; Serebrovskaya et al., 1998a,b; Volobuev, 1998; Chizhov and Bludov, 2000; Ragozin et al., 2000). Noted also is the use of IHT in the prophylaxis of professional occupational diseases (Berezovsky et al., 1985; Karash et al., 1988; Serebrovskaia et al., 1996) and in sports (Volkov et al., 1992; Radzievskii, 1997; Kolchinskaya et al., 1998, 1999). Recent reviews from Western Europe and North America are also given (Bavis et al., 2001; Clanton and Klawitter, 2001; Fletcher, 2001; Cozal and Cozal, 2001; Mitchell et al., 2001; Neubauer, 2001; Prabhakar, 2001; Prabhakar et al., 2001; Wilber, 2001).
During successive altitude exposures, compared with the initial exposure, the higher ventilation and blood arterial oxygen saturation, together with the lower blood Pco2, implied that ventilatory sensitivity to hypoxia had been increased.
In the intervening years to the present, intermittent hypoxia has been used extensively in the Soviet Union and the CIS not only for altitude pre acclimatization (Gorbachenkov et al., 1994), but also it has been proposed for treatment of a variety of clinical disorders, including chronic lung diseases and bronchial asthma in children and adults (Meerson et al., 1989; Anokhin et al., 1992; Berezovskii and Levashov, 1992; Donenko, 1992; Ehrenburg and Kordykinskaya, 1992; Fesenko and Lisyana, 1992; Redzhebova and Chizhov, 1992; Vinnitskaya et al., 1992; Lysenko et al., 1998; Serebrovskaya et al., 1998b; Chizhov and Bludov,2000; Ragozin et al.,2000, 2001), hypertension (Meerson et al., 1989; Potievskaya and Chizhov, 1992; Rezapov, 1992), emotional disorders (Gurevich et al., 1941), diabetes mellitus (Kolesnyk et al., 1999; Zakusilo et al., 2001), Parkinson’s disease (Kolesnikova and Serebrovskaya, 1998; Serebrovskaya et al., 1998a), inflammatory processes (Tkatchouk, 1994; Tsvetkova and Tkatchouk, 1999), radiation toxicity (Karash et al., 1988; Sutkovyi et al., 1995; Serebrovskaia et al., 1996; Strelkov, 1997; Strelkov and Chizhov, 1998), and certain occupational diseases (Berezovsky et al., 1985; Karash et al., 1988; Rushkevich and Lepko, 2001).
If so, then in normal humans only a few minutes of daily hypoxic exposure rapidly induces detectable increments in hypoxic ventilatory response, a hallmark of altitude acclimatization.
Hypocapnia occurs with altitude acclimatization and ventilation remains increased for days after the subjects return to sea level. By contrast, in the two above studies, eucapnia was maintained during the hypoxic exposures and neither normoxic venilation nor normoxic PC02 was altered by IHT, suggesting that only the hypoxemia and not changes in PC02 (or pH) were involved.
Changing CO2, either for the carotid body or the brain, did not induce ventilatory acclimatization to hypoxia. The work from Bisgard’s laboratory suggested that ventilatory acclimatization to hypoxia in the goat depends almost exclusively on the carotid body’s response to low oxygen. If similar mechanisms operate in humans, then ventilatory acclimatization to hypoxia, operating via the carotid body and independent of changes in pH or PCO2, can be induced by IHT. What is remarkable is that such brief periods of hypoxia can have such clearly measurable increases in the ventilatory response to hypoxia.
In addition to increasing hypoxic ventilatory sensitivity, CIS investigators have reported that IHT increases tidal volume and alveolar blood flow during exercise, improves matching of ventilation to perfusion, increases lung diffusion capacity, redistributes peripheral blood flow during exercise, decreases heart rate, increases stroke volume, and increases blood erythrocyte counts (Volkov et al., 1992; Kolchinskaya, 1993; Radzievskii 1997; Kolchinskaya et al., 1999; Maluta and Levashov, 2001). These effects have been considered to be beneficial in training athletes (Volkov et al., 1992; Radzievskii, 1997). Such findings await independent confirmation from others.
The spectral analysis suggested that after IHT there was greater parasympathetic preponderance during the hypoxic challenge than in the control group. These novel studies conducted in Ukraine suggested that IHT mimicked the usual acclimatization to high altitude, with its primarily greater parasympathetic activity (Reeves, 1993; Hughson et al., 1994). Such activation of the parasympathetic system by IHT was supported by experiments in rats (Doliba et al., 1993; Kurhalyuk et al., 2001a, b, see below).
Among these effects are that brief hypoxic stimuli of only several minutes per day for only a few days give responses that last many days, even weeks, and also that IHT apparently affects a multitude of normal functions and disease states.
This work, as well as more recent studies (Lukyanova, 1997; Sazontova et al., 1997; Kondrashova et al., 1997; Temnov et al., 1997; Lebkova et al., 1999), indicated that the basic molecular response to any type of hypoxic challenge involves the mitochondrial enzyme complexes (MchEC). There is evidence that energy metabolism under acute hypoxia is affected even before a significant decrease in oxygen consumption becomes measurable and before cytochrome c oxidase (CO) activity is significantly reduced.
In the cascade of hypoxia-induced metabolic alterations, MchEC I is most sensitive to intracellular oxygen shortage. The reversible inhibition of MchEC I leads to both the suppression of reduced equivalent flux through the NAD-dependent site of the respiratory chain and the emergency activation of compensatory metabolic pathways, primarily the succinate oxidase pathway. The switch of energy metabolism to this pathway is the most efficient energy-producing pathway available in response to a lack of O2 (Lukyanova et al., 1982).
Skulachev (1996) proposed a two-stage mechanism that allows mitochondria to regulate O2 concentrations and to protect against oxidative stress: (1) «soft» decoupling of oxidative phosphorylation for «fine-tuning» and (2) decrease of the reduction level of respiratory chain components by opening nonspecific mitochondrial inner membrane pores as a mechanism to cope with massive O2 excess.
However, parallel nonenzymatic processes result in O2 formation. This is especially the case when 02 concentrations reach the capacity of the respiratory chain enzymes. Reduction in O2 concentrations leads to an exponential decrease in radical formation. Skulachev (1995) hypothesizes that mitochondria have a mechanism for «soft» decoupling in stage 4 of the respiratory chain. This mechanism prevents the complete inhibition of respiration, the complete reduction of respiratory carriers, and the accumulation of reactive compounds such as ubisemiquinone (CoQ·-). Such a mechanism will be activated, for example, if the capacity of the respiratory chain is decreased due to a reduced availability of ADP.
In contrast to the constriction of capillaries, which prevents undesirably high O2 concentrations in tissue, «soft» decoupling allows fine-regulation on an intracellular level.
Adaptation to hypoxia by an intermittent hypoxic challenge is associated with the expression of, and a shift toward, enzyme isoforms that can efficiently function in a mitochondrial environment with high concentrations of reduced equivalents as generated during hypoxia. This prevents inactivation of the MchEC and may constitute one of the adaptation mechanisms triggered by intermittent hypoxia.
One of the most significant peculiarities of adaptation to intermittent hypoxia is free-radical processes.
The periods of reoxygenation could lead to oxygen radical formation, which might be analogous to that occurring with normoxic reperfusion of transiently hypoxic or ischemic tissues (Belykh et al., 1992; Meerson et al., 1992a). If periods of hypoxia followed by normoxia led to formation of oxygen radicals, but if the hypoxia were much briefer than the periods of normoxia, and if the exposure sequence were repeated over days, then one might expect that antioxidant defenses could be enhanced much more effectively than in sustained hypoxia.
In a recent study rats were given shorter hypoxic exposures: 15 min five times daily for 14 d (Kurhalyuk and Serebrovskaya, 2001). When they were subsequently challenged by exposure to 7% oxygen, blood catalase and glutathione reductase activity were increased and malon dialdehyde concentration was half that of non-IHT controls. The findings were consistent with the concept that intermittent hypoxia stimulates increased antioxidant defenses.
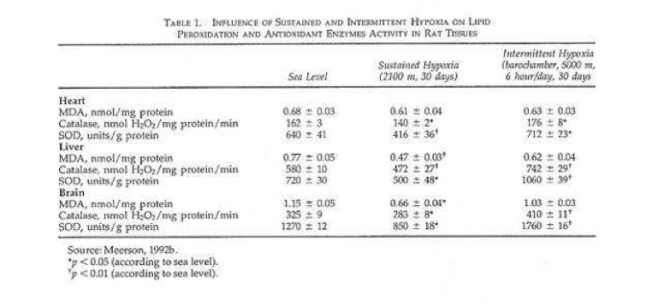
While there was considerable individual variability in the findings (Table 2), our indexes of oxidant stress before IHT were higher in the Chernobyl workers. We used a program of IHT: isocapnic, progressive, hypoxic rebreathing lasting for 5 to 6 min until inspired air O2 reached 8% to 7%, with three sessions, separated by 5 min, of normoxia, per day for 14 consecutive days. The use of IHT was accompanied by a decrease of spontaneous and hydrogen peroxide-initiated blood chemiluminescene, as well as considerable reduction of MDA content (Table 2). Of interest, more recent study on patients with bronchial asthma, who also were characterized by indexes suggestive of oxidative stress, have shown that similar IHT produced the increase of superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity by nearly 70%. This increase correlated with a decrease in MDA content (r = -0.61, P< 0.05) (Safronova et al., 1999; Serebrovskaya et al., 1999c).
Thus studies in humans and in tissues have shown that adaptation to intermittent hypoxia induces increased antioxidant defenses, acceleration of electron transport in the respiratory chain, stabilization of cellular membranes, and Ca2+ elimination from the cytoplasm. These data served as the basis for IHT in the treatment of various diseases in which free-radical production might be anticipated, for example, bronchial asthma and post-Chernobyl syndromes.
Recent studies have shown the following principal results: (1) adaptation to intermittent hypobaric hypoxia stimulates NO production in the organism; (2) excessive NO synthesized in the course of adaptation is stored in the vascular wall; (3) adaptation to hypoxia prevents both NO over-production and NO deficiency, resulting in an improvement in blood pressure; and (4) effects of intermittent hypoxia on mitochondrial respiration are mediated mainly by NO-dependent reactions (Manukhina et al., 1999, 2000a,b; Malyshev et al., 2000; Ikkert et al., 2000; Smirin et al., 2000; Kurhalyuk and Serebrovskaya, 2001; Kurhalyuk et al., 2001b; Serebrovskaya et al., 2001).
A somewhat different hypothesis has also been suggested, that the electron transport function of the myocardial respiratory chain in the NAD-cytochrome-b area is limited to a greater extent in animals poorly tolerant to hypoxia than in those that are not. In intolerant animals, even mild hypoxia leads to diminution of the oxidative capacity of the respiratory chain and of ATP production and, as a consequence, to a suppression of the energy-dependent contractile function of the myocardium. In animals more tolerant of hypoxia, this process is less manifest and develops very slowly, which confirms the lesser role of NAD-dependent oxidation of substrates in the metabolism of the myocardium of these animals (Korneev et al., 1990).
Taken together these studies suggest that IHT induces increased ventilatory sensitivity to hypoxia in the absence of Pco2 or pH changes; that it induces other hypoxia-related physiological changes such as increased hematopoiesis and decreased plasma volume and increase in alveolar ventilation and lung diffusion capacity; and that it may be useful in the management of certain disease states. The effects appear to be mediated, at least in part, through release of reactive oxygen species, which then induce an increase of antioxidant defenses. In addition, IHT appears to induce changes within mitochondria, possibly involving NAD-dependent metabolism, that increase the efficiency of oxygen utilization in ATP production.
Response of skeletal muscle mitochondria to hypoxia
Alt om hvordan mitochondrier reagerer på hypoxi, inkludert under trening. Nevner ROS, kapillærer, oxygencascade, HIF-1,tibetanere og høydetreningmen ingen ting om CO2. Nevner også hypoxi inntrer 20s etter trening starter – ref HIIT.
http://ep.physoc.org/content/88/1/109.long
In contrast to earlier assumptions it is now established that permanent or long-term exposure to severe environmental hypoxia decreases the mitochondrial content of muscle fibres. Oxidative muscle metabolism is shifted towards a higher reliance on carbohydrates as a fuel, and intramyocellular lipid substrate stores are reduced. Moreover, in muscle cells of mountaineers returning from the Himalayas, we find accumulations of lipofuscin, believed to be a mitochondrial degradation product. Low mitochondrial contents are also observed in high-altitude natives such as Sherpas.
In these subjects high-altitude performance seems to be improved by better coupling between ATP demand and supply pathways as well as better metabolite homeostasis.
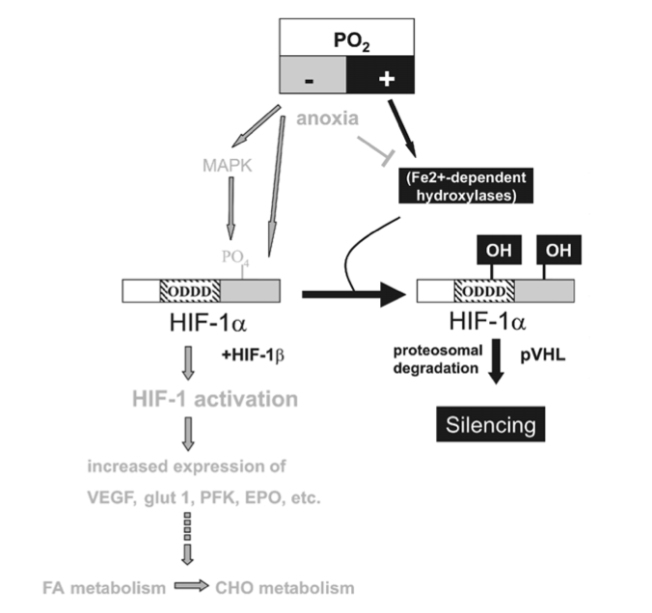
The hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) has been identified as a master regulator for the expression of genes involved in the hypoxia response, such as genes coding for glucose transporters, glycolytic enzymes and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). HIF-1 achieves this by binding to hypoxia response elements in the promoter regions of these genes, whereby the increase of HIF-1 in hypoxia is the consequence of a reduced degradation of its dominant subunit HIF-1a.
A further mechanism that seems implicated in the hypoxia response of muscle mitochondria is related to the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in mitochondria during oxidative phosphorylation. How exactly ROS interfere with HIF-1a as well as MAP kinase and other signalling pathways is debated.
The current evidence suggests that mitochondria themselves could be important players in oxygen sensing.
The focus on mitochondria neglects the fact that for the dominant function of mitochondria, aerobic ATP re-synthesis, the mitochondrial organelle cannot function independently. It is embedded, at least in animal phyla, in a systems physiological context. Mitochondria house the final biochemical steps in the production of reducing equivalents that react at the terminal oxidases of the respiratory chain with molecular oxygen provided by the respiratory system from the environment.
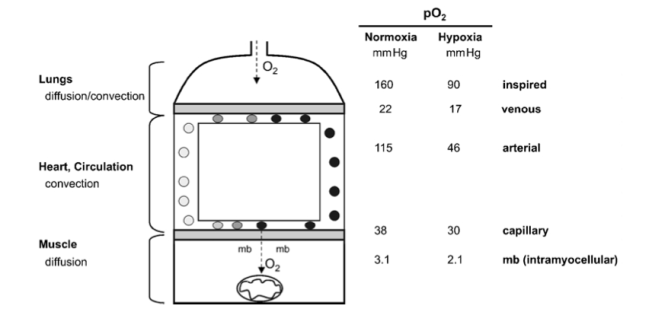
In mitochondria, O2 finally disappears and oxygen partial pressure goes to zero (Fig. 1). Mitochondria thus are an effective oxygen sink and this allows organisms to use all of the available oxygen partial pressure of the actual environment to drive the respiratory cascade from lungs through circulation to the mitochondria (Taylor & Weibel, 1981).
Figure 1
The pathway of oxygen. Simplified model of the oxygen transport pathway showing the principal structures and the corresponding partial pressure of oxygen (PJ) in these compartments, during maximal exercise, while breathing normoxic or hypoxic room air. mb, myoglobin. The data are derived from Richardson et al. (1995).
What is known is that isolated mitochondria do not need more than a few torr of O2 partial pressure for full function (Gayeski & Honig, 1997). Similarly, it is generally acknowledged that assessing mitochondrial function in hypoxia in cultured cells requires the lowering of the oxygen pressure at the cell surface to values between 0.5 and 5 Torr, values completely incompatible with the survival of all but a few highly specialized species (Boutilier & St Pierre, 2002).
In the context of this review we mostly neglect the hypoxic response of the microvasculature as well as the cardio- vascular and pulmonary system, which all conspire to maintain mitochondrial function under hypoxic conditions (Hochachka, 1998).
With ‘short- term’ hypoxia we refer to continuous bouts of hypoxia exposure lasting from minutes to hours (such as during a physical exercise bout), whereby during most of the day subjects are subjected to normoxic conditions.
With the term ‘intermittent’ hypoxia we designate experimental protocols whereby short periods of hypoxia (minutes) are interspersed with similarly short periods of normoxia. The physiological effects of inter- mittent hypoxia interventions have not yet been well defined. In particular, these types of interventions have not to our knowledge been analysed with regard to changes of the mitochondrial compartment. This literature will thus not be reviewed here (see Serebrovskaya, 2002).
One of the first notions of a change of muscle oxidative capacity with hypoxia is found in Reynafarje’s (1962) landmark paper on muscle adaptations in Peruvian miners. He found cytochrome c reductase activity (+78 %) and myoglobin content (+16%) to be significantly increased in biopsies of sartorius muscle of permanent high-altitude residents as compared to low-landers. This paper, together with data of larger muscle capillary densities in guinea pigs native to the Andeas as compared to data from low-land control animals (Valdivia, 1958), had a strong impact on physiologists’ thinking for at least two decades.
When it became clear towards the end of the sixties, that endurance-type exercise was also a potent stimulator of muscle mitochondrial enzyme activity (Holloszy, 1967), the connection was made that local tissue hypoxia provoked by exercise might be an important signal for mitochondrial proliferation under heavy exercise conditions.
The capillary density (i.e. the number of capillaries counted per unit area of muscle fibre) was indeed found to be increased in post-expedition samples. However, this was not due to capillary neo-formation since the capillary to muscle fibre ratio was unchanged. What had occurred over the time of the expedition was a significant loss of muscle fibre cross- sectional area. Hence, the same number of capillaries supplied a smaller tissue space. In addition, we found a decrease of mitochondrial volume density, which led to a total loss of muscle mitochondrial volume of close to 30 %.
This adaptation was suggested to represent an anti-apoptotic mechanism allowing protection against the lack of oxygen in oxidative muscles (Riva et al. 2001).
We would assume that the increased transcription of genes involved in the metabolic pathways favouring glucose metabolism in muscle cells is responsible for the observed shift towards glucose metabolism in organisms at altitude. The functional advantage of this adaptation would be a larger ATP yield per molecule of oxygen (Wilmore & Costill, 1994). It has recently been shown that protein expression of the enzymes and transporters of lactate, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and monocarboxylate transporters (MCT1, 2 and 4), is affected in a tissue-specific manner by long-term exposure to hypobaric hypoxia (McClelland & Brooks, 2002). These findings are broadly compatible with the idea that hypoxia induces mechanisms favouring glucose utilization in muscle cells.
Despite the low muscle mitochondrial oxidative capacity, physical performance capacity of native high-land populations at altitude is excellent. A number of physiological mechanisms have been invoked to explain the ‘paradoxical’ finding of superior aerobic performance in hypoxia despite modest muscle oxidative capacities (Hochachka et al. 2002). Hochachka et al. (1998) describe systemic mechanisms, among them being a blunted hypoxia ventilatory and pulmonary vasoconstrictor response as well as an up-regulation of erythropoietin expression, which help native high-land populations to excel at altitude. At the level of muscle tissue it is suggested that the control contributions from cellular ATP demand and ATP supply pathways are up-regulated whereas the contribution of control steps in O2 delivery are down-regulated (Hochachka et al. 2002). This leads to an improved coupling between ATP demand and supply pathways and better metabolite (i.e. lactate, adenylates) homeostasis.
We thus decided to explore hypoxia protocols under which hypoxia was present only during the exercise session but not during recovery (e.g living low–training high). Analysis of pre- and post- training biopsies of m. vastus lateralis revealed that total mitochondria increased significantly in all groups; in contrast, subsarcolemmal mitochondria, i.e. those located near capillaries, increased significantly only in those groups training under hypoxic conditions, irrespective of training intensity. Noticeably, the group which trained at high intensity in hypoxia showed the highest increase in total mitochondrial volume density (+59 %) and capillary length density was increased significantly in this group only (+17.2 %) (Geiser et al. 2001; Vogt et al. 2001).
Several independent lines of evidence suggest the occurrence of ‘local hypoxia’, i.e. a drop in intramyocellular oxygen pressure with exercise.
This finding of a low muscle oxygen tension during exercise is supported by more recent data using 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy which demonstrates that myoglobin desaturation occurs within 20 s of onset of exercise in human quadriceps muscle (Richardson et al. 1995).
Mitochondria, the oxygen sink, are more prevalent in oxidative fibres by a factor of at least three, and even within fibres they are clustered in the fibre periphery close to the capillaries (Howald et al. 1985).
Figure 3
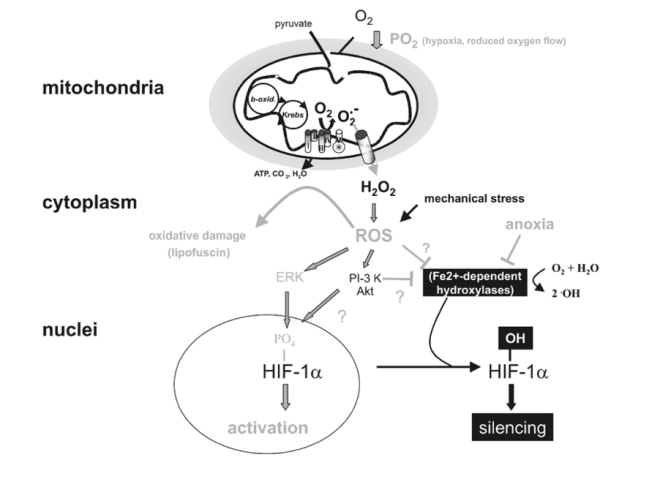
HIF-1a-mediated oxygen sensor and hypoxia-inducible gene expression. Oxygen stabilizes hypoxia- inducible factor 1a (HIF-1a) through Fe2+-dependent proline hydroxylases and asparaginyl hydroxylase(s) which hydroxylate HIF-1a within its oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODDD) and C-terminal portion, respectively. Such modification causes recruitment of the von Hippel-Lindau tumour- suppressor protein (pVHL), which targets HIF-1a for proteosomal degradation thereby silencing HIF-1a activity. Conversely, hypoxia causes a stabilization of HIF-1a and activates the MAPK pathway which enhances the transcriptional activity of HIF-1a through phosphorylation. Both mechanisms contribute to transcriptional activation of downstream angiogenic factor (VEGF), erythropoietin (EPO), glucose transporters (glut 1 and 3) and glycolytic genes (PFK) via HIF-1a/HIF-1b dimers (HIF-1). Moreover, lack of oxygen (anoxia) causes HIF-1a stabilization, possibly by reducing the activity of hydoxylases by depleting their substrate O2.
In vitro experiments show that an activation of HIF-1 leads to an up-regulation of anaerobic enzymes of the glycolytic pathway (Wenger, 2002).
To date there is no clear-cut explanation for the paradoxical finding of increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in hypoxia as there is controversy about whether hypoxia, in fact, causes an increase or a fall in ROS production (Archer & Michelakis, 2002). Also the mechanisms by which ROS and cytosolic H2O2 levels are involved in stabilization/activation and eventual degradation/silencing of HIF-1a and other redox-sensitive transcription factors are controversially discussed (Chandel et al. 2000; Kietzmann et al. 2000).
It is reported that ~2% of the O2 used by the mitochondrial electron transport chain creates ROS and in particular the superoxide radical, due to its incomplete reduction (see Kietzmann et al. 2000; Archer & Michelakis, 2002; reviewed in Abele et al. 2002). The superoxide anion (O2•_) radical is very unstable and is rapidly converted either spontaneously or after its export into the cytoplasm by mitochondrial and cytoplasmic superoxide dismutases, MnSOD and Cu/ZnSOD, to the more stable H2O2.
Recent findings in hepatoma cells indicate a small (approximately 2.5-fold) and transient increase in ROS after 40–50 min of hypoxia onset (0.5 % O2; Vanden Hoek et al. 1998). These and subsequent in vitro experiments in the same system point to mitochondria, and to respiratory complex III of the electron transport chain in particular, as the source of ROS production in hypoxia (Chandel et al. 2000).
Figure 4
Targets of mitochondrial ROS production. Incomplete reduction of O2 during normal metabolic conversion of pyruvate in mitochondria gives rise to a low level of superoxide anion (O2•_). Exposure of cells to hypoxia increases the aberrant production of O2•_ at the mitochondrial electron chain complex III. Catalysed or spontaneous dismutation of the unstable superanion and export via anion channels enhances the concentration of cytosolic H2O2 and other reactive oxygen species (ROS). Increased ROS may increase the level of oxidatively damaged lipids (lipofuscin) or activate downstream redox-sensitive signal transduction events. For example ROS stabilize HIF-1a possibly by interfering with the activity of Fe2+-dependent proline hydroxylases. ROS may also activate the MAPK or PI-3K/Akt pathway, which enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1a through its phosphorylation. Lastly, mechanical stress may also increase ROS production which may influence HIF-1a activation.
Clearly there is evidence pointing to a role of mitochondria as oxygen sensors by modulation of ROS production.
Recently, evidence for increased oxidant production in rat skeletal muscle during prolonged exercise has been provided, with both the mitochondrial respiratory chain and the NADPH oxidase as potential sources for oxidants (Bejma & Ji, 1999). This argues for ROS production in skeletal muscle due to local tissue hypoxia.
Differences in the control of breathing between Himalayan and sea-level residents
Om hvordan langvarig høydeopphold utvisker sensitiviteten til CO2.
http://jp.physoc.org/content/588/9/1591.full
Highlanders had lower mean ± S.E.M.ventilatory sensitivities to CO2 than lowlanders at both isoxic tensions (hyperoxic: 2.3 ± 0.3 vs. 4.2 ± 0.3 l min−1 mmHg−1, P = 0.021; hypoxic: 2.8 ± 0.3 vs. 7.1 ± 0.6 l min−1mmHg−1, P < 0.001), and the usual increase in ventilatory sensitivity to CO2 induced by hypoxia in lowlanders was absent in highlanders (P = 0.361).
Furthermore, the ventilatory recruitment threshold (VRT) CO2 tensions in highlanders were lower than in lowlanders (hyperoxic: 33.8 ± 0.9 vs. 48.9 ± 0.7 mmHg, P < 0.001; hypoxic: 31.2 ± 1.1 vs. 44.7 ± 0.7 mmHg, P < 0.001).
We conclude that control of breathing in Himalayan highlanders is distinctly different from that of sea-level lowlanders. Specifically, Himalayan highlanders have decreased central and absent peripheral sensitivities to CO2. Their response to hypoxia was heterogeneous, with the majority decreasing their VRT indicating either a CO2-independent increase in activity of peripheral chemoreceptor or hypoxia-induced increase in [H+] at the central chemoreceptor.
Control of breathing in humans can be broadly divided into chemoreflex and non-chemoreflex drives to breathe (Fig. 1) (Lloyd & Cunningham, 1963). Non-chemoreflex breathing stimuli include a wakefulness drive (Longobardo et al. 2002), voluntary (cortical) drive (Shea, 1996) and hormonal factors (Jensen et al. 2008), as well as neural and humoral mediating factors that are especially important in the control of breathing during exercise (Bell, 2006; Dempsey, 2006; Haouzi, 2006). The chemoreflex drive to breathe can be further divided into central and peripheral chemoreceptor drives. Both central and peripheral chemoreceptors respond to changes in the hydrogen ion concentration ([H+]) in their immediate environments (Torrance, 1996; Nattie & Li, 2009).
In contrast to the central chemoreceptors, peripheral chemoreceptors are also sensitive to changes in arterial  (
( ) via a hypoxia-mediated increase in their sensitivity to [H+] (Cunningham, 1987; Torrance, 1996; Kumar & Bin-Jaliah, 2007), and hyperoxia (
) via a hypoxia-mediated increase in their sensitivity to [H+] (Cunningham, 1987; Torrance, 1996; Kumar & Bin-Jaliah, 2007), and hyperoxia ( ≥ 150 mmHg) effectively silences this response (Lloyd & Cunningham, 1963; Mohan & Duffin, 1997).
≥ 150 mmHg) effectively silences this response (Lloyd & Cunningham, 1963; Mohan & Duffin, 1997).
Central and peripheral chemoreceptor neural drives are integrated in the medulla to provide the total chemoreflex neural drive (Fink, 1961; Shea, 1996; Mohan & Duffin, 1997; Orem et al. 2002) that, in combination with non-chemoreflex drives, provides ventilatory drive to respiratory muscles.


Figure 3. Hypercapnic ventilatory response The graph displays two isoxic responses: hyperoxic ( = 150 mmHg) representing central chemoreflex response, and hypoxic (
= 150 mmHg) representing central chemoreflex response, and hypoxic ( = 50 mmHg) representing the addition of central and peripheral chemoreflexes responses. The slope of each isoxic response represents sensitivity of the chemoreflex to CO2. The inflection point at which ventilation starts to increase in response to increasing
= 50 mmHg) representing the addition of central and peripheral chemoreflexes responses. The slope of each isoxic response represents sensitivity of the chemoreflex to CO2. The inflection point at which ventilation starts to increase in response to increasing  is the ventilatory recruitment threshold (VRT), where the chemoreflex neural drive to breathe exceeds a drive threshold and starts to produce an increase in pulmonary ventilation. Ventilation below VRT represents non-chemoreflex drives to breathe and is known as the basal ventilation. The differences in ventilation between isoxic rebreathing lines at any given isocapnic
is the ventilatory recruitment threshold (VRT), where the chemoreflex neural drive to breathe exceeds a drive threshold and starts to produce an increase in pulmonary ventilation. Ventilation below VRT represents non-chemoreflex drives to breathe and is known as the basal ventilation. The differences in ventilation between isoxic rebreathing lines at any given isocapnic  can be used to calculate the hypoxic ventilatory response (indicated by vertical arrows). Note that the choice of isocapnic
can be used to calculate the hypoxic ventilatory response (indicated by vertical arrows). Note that the choice of isocapnic  affects the magnitude of the measured HVR even within the same subject (Duffin, 2007), with higher HVRs measured at higher isocapnic
affects the magnitude of the measured HVR even within the same subject (Duffin, 2007), with higher HVRs measured at higher isocapnic  values in the illustrated example. Note also that the magnitude of HVR provides little information about the characteristics of the control of breathing model, as HVR magnitude is dependent on the combination of central and peripheral chemoreflex responses.
values in the illustrated example. Note also that the magnitude of HVR provides little information about the characteristics of the control of breathing model, as HVR magnitude is dependent on the combination of central and peripheral chemoreflex responses.
There was no difference in the non-chemoreflex drives to breathe between highlanders and lowlanders, as indicated by similar basal (below VRT) ventilations in the two populations (Table 2).
The highlanders had decreased VRTs compared to lowlanders during both hypoxic and hyperoxic rebreathing tests. The leftward shift of the VRTs in highlanders suggests that a lower  was required to exceed the VRT in highlanders compared to lowlanders. Since both central and peripheral chemoreceptors are actually [H+] sensors, interpretation of this result should consider the acid–base status in both populations. According to the Henderson–Hasselbach equation (Nunn, 1993), the relationship between [H+] and
was required to exceed the VRT in highlanders compared to lowlanders. Since both central and peripheral chemoreceptors are actually [H+] sensors, interpretation of this result should consider the acid–base status in both populations. According to the Henderson–Hasselbach equation (Nunn, 1993), the relationship between [H+] and  can be described as follows:
can be described as follows: where [HCO3−] is the bicarbonate ion concentration. In a hypothetical sea-level resident at sea-level, [H+] is approximately 40 nM l−1,
where [HCO3−] is the bicarbonate ion concentration. In a hypothetical sea-level resident at sea-level, [H+] is approximately 40 nM l−1,  is 40 mmHg and [HCO3−] is 24 mM l−1. At altitude, hypoxia-induced hyperventilation results in a reduction of
is 40 mmHg and [HCO3−] is 24 mM l−1. At altitude, hypoxia-induced hyperventilation results in a reduction of  that leads to a reduction in [H+] and respiratory alkalosis according to the above equation. Highlanders compensate for respiratory alkalosis by presumably reducing their [HCO3−] through increased renal excretion, thereby restoring the
that leads to a reduction in [H+] and respiratory alkalosis according to the above equation. Highlanders compensate for respiratory alkalosis by presumably reducing their [HCO3−] through increased renal excretion, thereby restoring the  /[HCO3−] ratio to sea-level values and normalizing [H+].
/[HCO3−] ratio to sea-level values and normalizing [H+].
For example, if hypoxia-induced hyperventilation reduced CO2 from 40 to 30 mmHg, and HCO3− fell from 24 to 18 mM l−1, then the overall ratio of CO2/HCO3− would be maintained at 5/3 as in sea-level lowlanders, but normal [H+] of 40 nM l−1 would be achieved at a lower  of 30 mmHg rather than 40 mmHg, as at sea-level. Considering that the highlanders in our study have an adapted acid–base status (Santolaya 1989), the observed difference in VRTs can be explained by the altered [H+]–
of 30 mmHg rather than 40 mmHg, as at sea-level. Considering that the highlanders in our study have an adapted acid–base status (Santolaya 1989), the observed difference in VRTs can be explained by the altered [H+]– relationship in highlanders compared to lowlanders, with the assumption that the chemoreceptor thresholds [H+] are similar (Duffin, 2005).
relationship in highlanders compared to lowlanders, with the assumption that the chemoreceptor thresholds [H+] are similar (Duffin, 2005).
The sensitivity of the central chemoreceptor to CO2, as indicated by the ventilatory sensitivity during hyperoxic rebreathing, was lower in highlanders compared to lowlanders (2.5 ± 0.4 vs. 4.2 ± 0.3 l min−1 mmHg−1, P = 0.011). Hyperoxia effectively silences the peripheral chemoreceptor (Lloyd & Cunningham, 1963; Mohan & Duffin, 1997), and therefore the ventilatory sensitivity measured during hyperoxic rebreathing can be taken as a measure of central chemoreceptor sensitivity (Duffin, 2007).
Since the ventilatory response to hypercapnia decreases with age (Nishimura et al. 1991; Jones et al. 1993; Poulin et al.1993; McGurk et al. 1995) and increases with weight (Marcus et al. 1994), the observed lower central CO2 chemosensivity in our highlander subjects may be the result of their older age and smaller body size.
Ventilatory response to hypoxia in highlanders was markedly different from that in lowlanders. Unlike lowlanders, who responded to hypoxia by increasing the sensitivity of their ventilatory response to CO2 (Mohan & Duffin, 1997), the highlanders seemed to decrease their VRT in response to hypoxia with no change in the sensitivity to CO2.
The ventilatory response to hypoxia in sea-level residents is mediated by peripheral chemoreceptors via an increase in the peripheral chemoreceptor sensitivity to [H+] (Cunningham, 1987; Torrance, 1996; Kumar & Bin-Jaliah, 2007). A lack of increase in ventilatory sensitivity to CO2 with induction of hypoxia in highlanders suggests that their peripheral chemoreceptors are relatively insensitive to CO2.
Other possible mechanisms of CO2-independent peripheral responses to hypoxia may include a hypoxia-induced increase in the carotid body tonic drive to breathe, changes in systemic hormonal mediators, an altered cerebral spinal fluid-buffering capacity at the central chemoreceptor or an alteration in cerebral vascular reactivity leading to a higher [H+] at central chemoreceptor.
Specifically, we showed that Himalayan highlanders have decreased central and absent peripheral chemoreceptor sensitivity to CO2, and that they are sensitive to hypoxia, albeit via a different mechanism than that observed in lowlanders at sea-level. A blunted central and an absent peripheral ventilatory sensitivity to CO2 in Himalayan highlanders may stabilize their ventilatory controller by reducing the overall gain in the feedback part of the controller circuit, thereby reducing altitude-related breathing instability (Ainslie & Duffin, 2009)
The non-chemoreflex drives to breathe were similar between Himalayan highlanders and sea-level lowlanders.
Human skeletal muscle intracellular oxygenation: the impact of ambient oxygen availability
Viktig studie som beskriver alt om hvordan oksygen-nivået synker fra innpust gjennom blodkar og ut til celler, og relasjonen til trening hvor cellene ikke mottar oksygenet pga lav CO2 som følge av hyperventillering.
http://jp.physoc.org/content/571/2/415.full
Intracellular oxygen (O2) availability and the impact of ambient hypoxia have far reaching ramifications in terms of cell signalling and homeostasis; however, in vivo cellular oxygenation has been an elusive variable to assess.
These data are the first to document resting intracellular oxygenation in human skeletal muscle, highlighting the relatively high PiO2 values that contrast markedly with those previously recorded during exercise (∼2–5 mmHg). Additionally, the impact of ambient hypoxia on PiO2 and the relationship between changes in SaO2 and PiO2 stress the importance of the O2 cascade from air to cell that ultimately effects O2 availability and O2 sensing at the cellular level.
Changes in intracellular oxygen availability have far reaching consequences likely involved in such diverse processes as angiogenesis (Richardson et al. 1999c; Wagner, 2001) and hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (Wang et al. 2005; Wolin et al. 2005).
Therefore, although it is known that musclePiO2 falls to very low values of 2–5 mmHg during exercising (Mole et al. 1999;Richardson et al. 2001), the starting point for skeletal muscle oxygenation or resting PiO2is, as of yet, unknown.
Hypoxia is both an important stimulus and a constant threat to the human body and its vital organs throughout life. Environmental changes such as exposure to high altitude reduce ambient O2 availability, while lung, vascular, and sleep disorders can result in hypoxia under normoxic conditions. It is known that hypoxia mediates adaptive changes in metabolism, O2 sensing and gene expression. However, although much research has examined the consequences of experimental hypoxic conditions, data documenting hypoxically mediated changes in cellular oxygenation in humans are sparse, if not non-existent.
Specifically, it was determined that in normoxia Mb was 9 ± 1% deoxygenated and this increased to 13 ± 3% in hypoxia. In our view, any degree of Mb deoxygenation supports the role of Mb as a facilitator of O2 diffusion, and thus the observation that Mb is somewhat desaturated in normoxia and furthermore that Mb desaturation increases in hypoxia is consistent with Mb playing a significant role in O2 transport from blood to cell.

Theoretically, because of the O2 cascade from air to tissue, graded reductions in FIO2 should ultimately alter in vivo O2 availability all the way to the myocyte (Richardson et al. 1995b).
In fact, this hypoxic ventilatory response (HVR) varies widely between individuals, and has been used to distinguish between those who will thrive and those who will perish at high altitude (Bartsch et al. 2001).
50% of the variance in PiO2 could be explained by the change in arterial PO2 (Fig. 4). Hence, the fall in skeletal muscle PiO2was attenuated in those subjects with a brisk HVR, making teleological sense and providing perhaps the first evidence, through arterial O2 saturation, of the importance of human HVR in terms of cellular O2 homeostasis.
Despite an apparently strong HVR in some subjects, the ambient hypoxia of 10% O2significantly reduced the average intracellular Mb saturation by ∼44% and calculated PiO2by ∼33%. Although the complete ramifications of such a change within resting muscle cells are unknown (cell signalling and growth factor responses) it is clear that such a perturbation, although relatively large, still leaves the cells far above the suggested ‘critical PO2’ (between 0.1 and 0.5 mmHg) below which muscle metabolism is compromised (Chance & Quistorff, 1978; Wilson et al. 1979; Richmond et al. 1999).
Taken together these data reinforce the concept that O2 availability and metabolism are more tightly coupled during exercise when PiO2 falls to low levels than at rest when there is a relative abundance of O2.
Specifically, in the current study a reduction in the ambient O2 to 10% resulted in an ∼11 mmHg change in PiO2 at rest (from 34 to 23 mmHg), whereas in previous investigations during exercise (using 12% O2) we have repeatedly seen closer to a ∼1 mmHg reduction (from 3 to 2 mmHg) (Richardson et al.1995b, 1999b, 2002).
This phenomenon may occur as a result of the mitochondrial transition from a somewhat quiescent state during rest to an active more governing role, in terms of determining PiO2, during exercise. Therefore, these data support the theory that during a hypoxic challenge resting PiO2 is most likely the simple consequence of ambient hypoxia upon passive diffusion, while during exercise the large increase in metabolic rate and subsequent O2consumption reduce PiO2 and facilitate O2 transport to a greater extent, somewhat staving off the effect of ambient hypoxia.
Inspiratory muscle training reduces blood lactate concentration during volitional hyperpnoea
Med pustetrening blir melkesyrekonsentrasjonen lavere under trening. 2 studier her, første fra 2008 og den andre fra 2012.
Den første nevner at melkesyre synker med opptil 59% (25+34%)
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18560878
Although reduced blood lactate concentrations ([lac(-)](B)) have been observed during whole-body exercise following inspiratory muscle training (IMT), it remains unknown whether the inspiratory muscles are the source of at least part of this reduction.
After 6 weeks, increases in [lac(-)](B) during volitional hyperpnoea were unchanged in the control group. Conversely, following IMT the increase in [lac(-)](B) during volitional hyperpnoea was reduced by 17 +/- 37% and 25 +/- 34% following 8 and 10 min, respectively (P < 0.05).
These findings suggest that the inspiratory muscles were the source of at least part of this reduction, and provide a possible explanation for some of the IMT-mediated reductions in [lac(-)](B), often observed during whole-body exercise.
Inspiratory muscle training abolishes the blood lactate increase associated with volitional hyperpnoea superimposed on exercise and accelerates lactate and oxygen uptake kinetics at the onset of exercise.
Den andre viser til en 15% laver melkesyrekonsentrasjon og at årsaken er pustemusklenes evne til å fjerne det.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21964908
Following the intervention, maximal inspiratory mouth pressure increased 19% in the IMT group only (P < 0.01). Following IMT only, the increase in [lac(-)](B) during volitional hyperpnoea was abolished (P < 0.05). In addition, the blood lactate (-28%) and phase II oxygen uptake (-31%) kinetics time constants at the onset of exercise and the MLSS [lac(-)](B) (-15%) were reduced (P < 0.05). We attribute these changes to an IMT-mediated increase in the oxidative and/or lactate transport capacity of the inspiratory muscles.
Inspiratory muscle training lowers the oxygen cost of voluntary hyperpnea
Nevner at innpustmuskel trening gir mindre oksygenbehov under trening og dermed mer utholdenhet. Innpustmuskler bruker opp mye av oksygenet kroppen trenger under trening så med svak pustefunksjon blir man fort sliten. Under maksimal trening krever pustemusklene 15% av oksygenet, men med pustetrening synker det til 8%. Den nevner at diafragma og pustemuskler blir sterkere og større. Den henviser også til studier som nevner at det gir mindre melkesyre. Noe av effekten kommer også av at man får en større reserve i lungene ved å øke inn- og utpust styrken.
http://jap.physiology.org/content/112/1/127.full
IMT significantly reduced the O2 cost of voluntary hyperpnea, which suggests that a reduction in the O2 requirement of the respiratory muscles following a period of IMT may facilitate increased O2 availability to the active muscles during exercise. These data suggest that IMT may reduce the O2cost of ventilation during exercise, providing an insight into mechanism(s) underpinning the reported improvements in whole body endurance performance; however, this awaits further investigation.
THE OXYGEN COST of breathing or energy requirement of the respiratory muscles are shown to increase relative to the level of ventilation (V̇E) and the work of breathing (Wb) (1, 8). During moderate-intensity exercise the respiratory musculature requires ∼3–6% of total oxygen consumption (V̇O2T), increasing to ∼10–15% at maximal exercise (1, 3).
Inspiratory muscle training (IMT) is an intervention that has been associated with improvements in whole body exercise performance (24, 31, 34), enhanced pulmonary oxygen uptake kinetics (5), reduced blood lactate concentrations (6, 24), diaphragmatic fatigue, and cardiovascular responsiveness (37).

The oxygen cost of voluntary hyperpnea (V̇O2RM) and V̇O2RM expressed as a percentage of total oxygen consumption (V̇O2T) graphed against V̇E at low (50% V̇O2 max), moderate (75% V̇O2 max), and high (100% V̇O2 max) exercise intensities for both IMT (A) and CON (B) groups, pre- and post-training (means ± SE).
•, Pre-IMT;
○, post-IMT;
▴, pre-CON;
Δ, post-CON.
To our knowledge this study is the first to investigate the influence of IMT on the oxygen cost of voluntary hyperpnea. The main findings of the present study are that the relationship between increasing ventilatory workloads and the O2 cost of voluntary hyperpnea is curvilinear in trained cyclists and that 6 wk of pressure threshold IMT significantly reduced the O2 cost of V̇E at high ventilatory workloads. Importantly, the finding that V̇O2RM is reduced at a V̇E above 50% V̇O2 max suggests that IMT may reduce the energy requirements of the respiratory musculature in maintaining a given V̇E.
The increase in energy expenditure as V̇E increases can be attributed to a variety of sources of respiratory muscle work, including the elastic recoil of the chest and lung wall, airway resistance (4,15), increased EELV (9), and high muscle shortening velocities (19, 23). It has been suggested that as tidal breathing approaches the maximal limits for inspiratory muscle pressure development and expiratory flow rates, energy expenditure may increase to overcome the additional respiratory muscle work (3). Conversely, if one or more of the additional sources of respiratory muscle work are reduced as a result of IMT, it is reasonable to suggest that the increase in the O2 cost maybe attenuated.
In the present study, following 6 wk of IMT, V̇O2RM was significantly reduced from pretraining values at submaximal and maximal levels of ventilation. The O2 cost of voluntary hyperpnea expressed as a percentage of V̇O2T was reduced by 1.5% at a V̇Ecorresponding to 75% V̇O2max following IMT. The greatest reduction in the O2 cost of voluntary hyperpnea was observed at V̇O2 max, where V̇O2RM was significantly reduced from 11% of V̇O2T to 8% V̇O2T following IMT.
Increased ventilatory demand was previously shown to elicit a sympathetically mediated metaboreflex (33), which increases heart rate and mean arterial pressure (MAP), reducing blood flow to the limb locomotor muscles during exercise (16) and potentially reducing whole body endurance performance (18). Furthermore, Witt et al. (37) showed that IMT attenuates this increase in HR and MAP, presumably by reducing or delaying the sympathetically mediated reflex.
The 22% increase in respiratory muscle strength shown in the present study is similar in magnitude to those previously reported using pressure-threshold IMT (11, 22, 30, 32, 37). Respiratory muscle structure has also been shown to change following IMT, with an increase in diaphragm thickness (11, 12) and hypertrophy of type II muscle fibers of the external intercostal muscles (27) being reported.
Aaron et al. (3) demonstrated that individuals who reached their reserve for expiratory flow and inspiratory muscle pressure development required 13–15% of V̇O2T compared with ∼10% of V̇O2T for non-flow-limited individuals. Thus, an increase in maximal expiratory flow rates or inspiratory pressure development would increase the ventilatory reserve, thereby increasing the maximal limits for ventilation.