Viktig studie om tummo som oppklarerer flere misforståelser og beskriver mange aspekter som tidligere ikke er beskrevet. Nevner bl.a. at vestlige også kan øke sin kroppstemperatur med disse teknikkene.
http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0058244
«Reliable increases in axillary temperature from normal to slight or moderate fever zone (up to 38.3°C) were observed among meditators only during the Forceful Breath type of g-tummo meditation accompanied by increases in alpha, beta, and gamma power.»
«Overall, the results suggest that specific aspects of the g-tummo technique might help non-meditators learn how to regulate their body temperature, which has implications for improving health and regulating cognitive performance.»
«The authors reported that three g-tummo meditators showed a dramatic increase of up to 8.3°C in peripheral body temperature (fingers and toes), more modest skin temperature increases of 1.9°C in the navel and lumbar regions, and no increase in rectal temperature. Unfortunately, these findings have subsequently been distorted in reports in other sources, possibly due to confusion between Fahrenheit and Centigrade scales or lack of clear specification regarding the anatomical sites of temperature measurement, leading to general claims of temperature increases during g-tummo ranging from “… up to 15 degrees only within a few moments of concentration” [3] to “17 degrees in peripheral body temperature” [8].»
«The visual effect of steaming sheets reported by eye-witnesses of the g-tummo ceremony cannot be taken as evidence of elevated body temperature. Wet sheets wrapped around a practitioner’s body would steam and dry due to the significant temperature difference between the wet sheets (heated by a human body) and the cold air outside, even if the practitioners simply maintain their normal body temperature.»
«Furthermore, they did not exceed the peripheral body temperature increases reported in clinical studies of (non-meditating) individuals who were able to increase hand or finger temperature by up to 11.7°C during biofeedback alone or in combination with hypnosis, mental imagery, or autogenic training[9]–[11]. Subsequent clinical research, however, reported that such peripheral temperature increases were primarily mediated by somatic (e.g., altered respiration and/or tensing and contracting of muscles) but not cognitive factors [12].»
«The g-tummo practice involves both somatic and neurocognitive components. The somatic component involves specialized breathing techniques as well as isometric exercises (i.e. exercises performed in static positions, rather than incorporating a range of motion) involving muscle tensing and contraction. The neurocognitive component involves meditative visualization requiring the generation and maintenance of mental images of flames at specific locations in the body accompanied by intense sensations of bodily heat in the spine.»
«Recent studies report that raising body temperature might be an effective way to boost immunity and treat infectious diseases and immunodeficiencies [13]–[15] as well as to induce synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus [16]. It has been long recognized that increased body temperature (in the zone of a slight fever) is associated with higher alertness, faster reaction time, and better cognitive performance on tasks such as visual attention and working memory [17]–[19]. »
«Some, but not all, of these monasteries test their practitioners’ capabilities at the end of a three-year retreat with a ceremony where the practitioners dry wet sheets. As a testament to the importance of the g-tummo practice at Gebchak nunnery, this ceremony is held annually, at dawn, and all of the experienced practitioners walk slowly for a few hours around the nunnery complex in −25°C to −30°C weather, wearing only short skirts and shoes and a wet sheet draped around their naked torsos.»
«The g-tummo practice is characterized by a special breathing technique, “the vase”, accompanied by isometric muscle contractions, where after inhalation, during a period of holding their breath (apnea), the practitioners contract both abdominal and pelvic muscles so that the protruding lower belly takes the shape of a vase or pot [1].»
Tilsvarerer akselereringsfasen i vårt tummo konsept.
«FB is forceful and vigorous, while GB is gentle and without any strain. Whereas the goal of FB is to raise “psychic heat”, the goal of GB is to maintain it. During FB, attention is focused on visualizing a rising flame that starts below the navel and with each breath rises up to the crown of the head, whereas GB is accompanied by visualization of the entire body being filled with a surging sensation of bliss and heat.»
Man kan enkelt måle kjernetemperatur selg med termometer i armhulen eller munnen.
«We recorded EEG activity of the meditators as well as their peripheral (left fifth finger) and core body temperature (left armpit) during g-tummo practices»
«Although not as precise as an internally taken rectal or oral measurement of core body temperature [20], axillary measurements are less intrusive. Importantly, they are not affected by muscle contractions (e.g., anal sphincter), or the airflow through the mouth, during the vase breathing.»
«The results indicated peripheral (finger) temperature increases between 1.2°C to 6.8°C during different conditions»
«During BFB, the maximum CBT increase was 1.14°C (participant #3) and the maximum temperature reached was 37.45°C (participant #4).»
«The maximum CBT increase from the beginning of the experiment to the end of MFB was 2.2°C (participant #3), and the maximum temperature reached was 38.30°C (participant #5).»

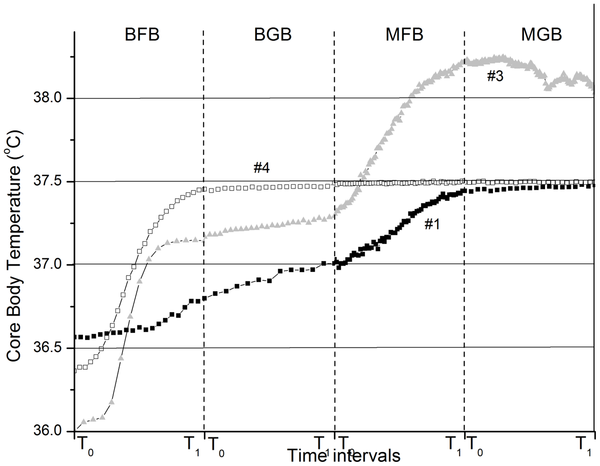
«Figure 3. CBT increases for Study 1 participants #1, #3, and #4 during BFB, BGB, MFB, and MGB performed in a continuous sequence.
Since the duration of each of the four practices varied from participant to participant, to simplify the figure presentation, the duration of each practice is rescaled from 0 to 1, with t0 the starting point of each practice, and t1 the ending point.»
«During FB (either BFB or MFB), participants’ CBTs typically exhibited a step-like pattern, with a period of steady temperature increase followed by a plateau or equilibrium phase corresponding to the “temperature saturation point”, above which the participants were not able to raise their CBT further despite their efforts to continue with FB. This pattern of CBT increases is very similar to that usually observed during induction of systemic hyperthermia (i.e., deliberate heating of a patient’s body to achieve an elevated core temperature for therapeutic purposes), where the equilibrium phase indicates the beginning of heat losses due to physiological mechanisms (e.g. vasodilation, evaporation) limiting the rate of heating that can be achieved, and thus protecting the body from excessively high temperatures [22].»
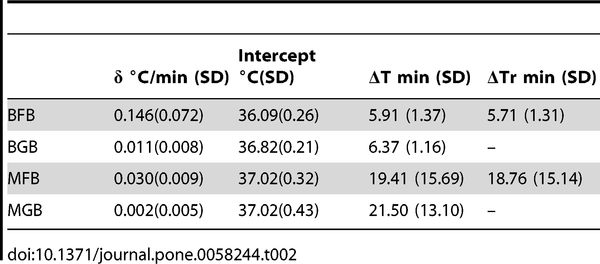
«we defined the rise time (ΔTr) as the time taken for the CBT to rise from 10% to 90% of its final value »
«In summary, the results suggest that although CBT increases during BFB were not as dramatic as during MFB, participants were able to produce body heat, utilizing only the somatic component of the FB practice (breathing and isometric techniques). However, the meditators were able to reach an elevated CBT, significantly above the normal axillary temperature, only during MFB practice. As for GB practice, consistent with practitioners’ reports that it is used to maintain (but not to increase) body heat, no significant changes in participants’ CBT were observed during either GB baseline or meditation.»
«Furthermore, the higher the increases in alpha power developed by participants during FB meditation, the larger their increases in CBT during FB meditation, while the CBT increases during BFB were achieved without any changes in alpha power. This suggests that different mechanisms may be affecting CBT increases during MFB versus BFB, and that meditative visualization characterized by significant increases in alpha power might uniquely contribute to overall CBT increases beyond the contribution of the vase breathing technique.»
«In summary, our findings indicate that the two parameters, apnea duration and increases in alpha power achieved during meditative visualization are significant predictors of the overall CBT increases during FB practice. The apnea duration is significantly related to the rate of CBT increase. The increase in alpha power developed during FB meditation is related to the CBT rise time, that is, it predicts how long the meditators are capable of sustaining their CBT increases without reaching equilibrium.»
«The average initial CBT of all the participants before BFB was 36.38°C (SD = 0.23), while the average temperature at the end of BFB reached 36.99°C (SD = 0.13), only marginally above the normal axillary temperature of 36.6°C in the healthy population [one sample two-tailed t(10) = 2.02, p = 0.07]. The maximum CBT reached during BFB was 37.02°C. «
«The average apnea duration of the participants was 30.38 sec (SD = 6.35), ranging from 19 to 41 sec; the apnea duration correlated with the rate of CBT increase during BFB: r = 0.60, p = 0.050.»
«all the Western non-meditator participants returned to their baseline CBT during the next 20 minutes. This is in contrast to Tibetan practitioners performing GB (Study 1) who did not show any decreases in their CBTs during either BGB or MGB (δ = 0.011°C/min and δ = 0.002°C/min respectively), and were able to maintain an elevated body temperature throughout the whole duration of MGB (on average 21.50 min). This further confirms that the GB practice facilitates maintenance of body temperature.»

«Figure 7. CBT increases during FB as performed by a Western non-meditator and a Western g-tummo practitioner.»
«In summary, the results of Study 2 indicate that the BFB technique brings about significant increases in CBTs not only in meditators but also in those individuals who do not have any prior experience in meditation. »
«As for the increased gamma activity observed during FB meditation, studies on meditation consider it a signature of “samadhi” (deep meditative states of consciousness), but the regions of increase have varied, with recent studies reporting in some cases a frontally distributed increase in gamma [28], and in other cases an increase in gamma at posterior and occipital electrodes [29]. »
«In the case of FB meditation, one of the possible mechanisms preventing heat loss could be the mental imagery of flames and heat. Indeed, previous research has regarded mental imagery as a potentially effective technique in influencing peripheral body temperature, blood flow, and local vasodilation [38]–[41]. »
«If future studies show that it is possible to self regulate CBT, by mastering vase breathing in conjunction with guided mental imagery without extensive meditation experience, it will open a wide range of possible medical and behavior interventions, such as adapting to and functioning in hostile (cold) environments, improving resistance to infections, boosting cognitive performance by speeding response time, and reducing performance problems associated with decreased body temperature as reported in human factor studies of shift work and continuous night operations[44], [45].»